EXCRETORY PARTS
The action of pissing
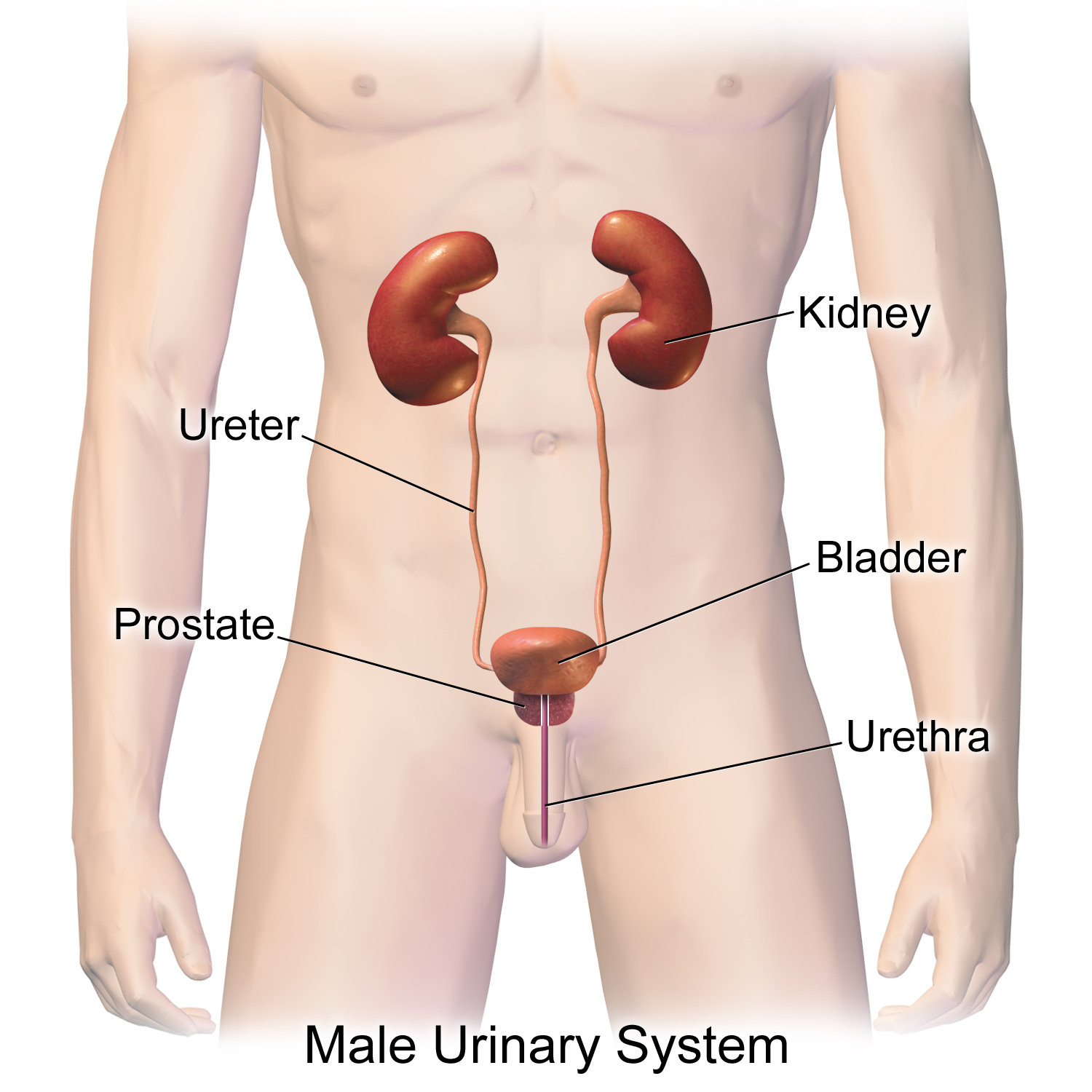
Ureters:
Ureters are muscular ducts that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In the adult, the ureters are usually 25-30 cm (10-12 in) long.
Urethra:
A tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Bladder:
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys prior to disposal by urination. It is a hollow muscular, and elastic organ, and sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra.
Skin:
Gives off bodily sweat or perspiration. Skin is the largest organ of the human body. It also protects the inner organs and tissues of the body.
Lungs:
Lungs give off carbon dioxide, a bodily waste, during respiration.
KIDNEY:
FUNCTIONS OF KIDNEYS
- Kidneys remove excess of water from body.
- Kidneys maintain proper pH of blood by removing the excess of acids and bases from blood.
- Kidneys remove other toxic substances from blood like urea, uric acid and ammonia.
- It maintains volume of extracellular fluid.
PENIS :
The penis is the male external excretory and sex organ. The penis contains the external opening of the urethra, which is used for urination and to deliver semen into the vagina of a female sexual partner.
VULVA:
Vulva, the external female genitalia that surround the opening to the vagina; collectively these consist of the labia majora, the labia minora, clitoris, vestibule of the vagina, bulb of the vestibule, and the glands of Bartholin.
THE ACTION OF DEFECATE:
REMEMBER THAT THE ACTION OF DEFECTS IS PART OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM